Mohamed Abbas | Architect Magento | Tech Blogger | Magento Trainer
Agentic RAG: The Next Evolution of Retrieval-Augmented AI
Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Agentic RAG) represents the next major step in AI systems, where large language models no longer follow a static “retrieve-then-answer” pattern. Instead, they dynamically plan their next actions, pull information from external sources, refine their queries, and continue this cycle until they reach a high-quality solution. Unlike traditional RAG pipelines that depend heavily on predefined instructions, Agentic RAG gives the model autonomy to choose the best path, tools, and strategies for solving the problem. This shift transforms the model from a passive responder into an active problem-solver capable of reasoning, evaluating, and improving its own output.
Introduction
Agentic RAG is designed for scenarios where accuracy, reliability, and multi-step reasoning are essential. It follows an iterative maker-checker loop in which the LLM continuously evaluates its progress, identifies missing information, and decides which tools or data sources to use next. This makes it ideal for correctness-first environments, complex database interactions, and extended workflows where the model must repeatedly refine its understanding of the task. By the end of this lesson, you will understand how Agentic RAG works, how it owns its reasoning process, and why it provides significant value in real-world AI systems.
What Is Agentic RAG?
At its core, Agentic RAG is an AI paradigm where the model autonomously drives the workflow. Instead of a fixed path, it uses a loop of LLM calls and tool calls, each step informed by the previous results. If the model identifies missing data, malformed queries, or incomplete reasoning, it will refine its approach, rewrite queries, switch retrieval methods, or even combine multiple tools such as SQL databases, vector search engines, and APIs. This ability to decide how to solve the problem—rather than blindly following a script—is what makes the system truly “agentic.”
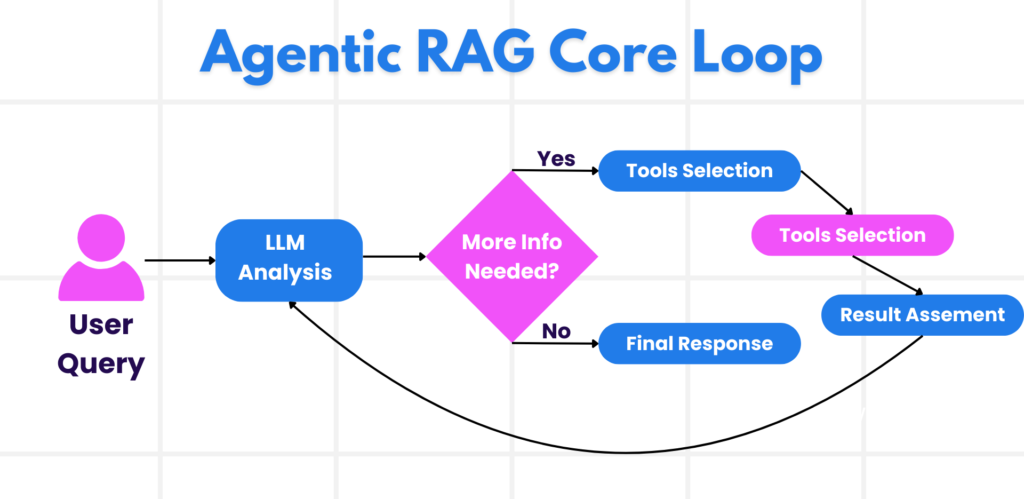
Owning the Reasoning Process
A defining feature of Agentic RAG is its ability to own its reasoning process. Traditional RAG relies heavily on humans to pre-script the workflow, specifying what to retrieve and when. But in an agentic system, the model determines the sequence of steps on its own.
To achieve this, the agent can:
- Retrieve information from multiple external sources
- Cross-check and correlate results
- Identify gaps or contradictions
- Refine the plan before finalizing the answer
For example, if asked to design a product launch strategy, the agent autonomously retrieves market trend data, fetches competitor insights, correlates sales metrics, synthesizes findings, and evaluates inconsistencies before presenting the final result. This entire chain is decided by the model based on what it discovers at each stage—not predetermined by a human.
Iterative Loops, Tool Integration, and Memory
Agentic RAG runs on a continuous interaction loop: the model takes the user’s prompt, checks what information is missing, calls tools such as vector search or SQL, evaluates the results, and decides whether to refine the query or move forward. This loop repeats until the model is satisfied. Crucially, the system maintains memory and state across each step, allowing it to avoid repetitive loops, remember failed attempts, and make more informed decisions over time. This creates an evolving understanding that enables the model to handle multi-step tasks without constant human intervention.
Where this becomes most important:
- Long-running workflows
- Tasks requiring multiple data sources
- Scenarios where intermediate failures are expected
- Complex SQL or API-based operations

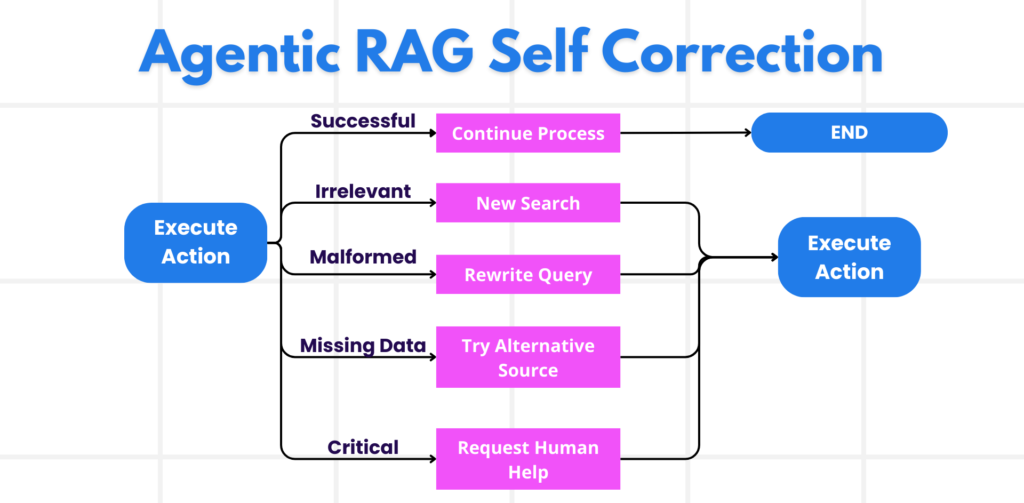
Handling Failures and Self-Correction
Failure is not an end-point in Agentic RAG—it’s part of the workflow. When the system encounters irrelevant results, malformed queries, or gaps in reasoning, it triggers self-correction. It may rewrite search queries, adjust SQL statements, or switch retrieval tools entirely. In some cases, it uses diagnostic functions to debug its own reasoning steps. And when uncertainty remains high, the system can escalate for human review, integrating that feedback into the ongoing session. This self-correcting loop makes Agentic RAG far more robust than traditional, one-shot retrieval systems.
Boundaries and Practical Limits
While Agentic RAG offers autonomy within a workflow, it is still bounded by the tools, data sources, and policies defined by developers. It cannot invent new tools or operate beyond its domain constraints. Rather, its intelligence lies in orchestrating the resources it has access to. It respects guardrails, adheres to compliance rules, and operates within the infrastructure designed for it. Its autonomy is domain-specific—not general intelligence—but within that domain, it excels.
Where Agentic RAG Shines
Agentic RAG delivers the most value in environments that demand accuracy, iteration, and multi-source reasoning. It performs especially well in regulatory analysis, compliance workflows, legal research, and financial intelligence, where correctness matters more than speed. It also thrives in complex database operations, where queries often need refinement, and in long-running workflows, where the task evolves as new information emerges. In these scenarios, its ability to retrieve, evaluate, refine, and repeat becomes a significant advantage.
Quick scenarios where it clearly outperforms traditional RAG:
- When multiple retrieval hops are required
- When data quality is inconsistent
- When the task evolves during execution
- When structured + unstructured data must be combined
Governance, Transparency, and Trust
Because Agentic RAG systems make independent decisions, governance becomes essential. These systems must provide visible reasoning steps, audit trails of tool calls, and transparency around the sources they consulted. Developers must ensure balanced retrieval, bias control, responsible data usage, and consistent human oversight for sensitive tasks. Tools such as tracing, observability dashboards, and content safety checks help maintain trust and ensure the system’s decisions remain aligned with organizational policies.
Conclusion
Agentic RAG is the next evolution of intelligent AI systems—adaptive, iterative, and able to own its reasoning process. By moving beyond static prompts and predefined workflows, it enables richer, more dynamic, and more accurate interactions with data. Although it operates within human-defined boundaries, its ability to autonomously refine queries, integrate tools, and produce well-grounded outputs makes it an invaluable tool for enterprises and advanced AI applications. As organizations demand more intelligence, reliability, and autonomy from AI, Agentic RAG will become one of the most powerful paradigms shaping the future of AI-driven decision-making.
